Red Rock Resorts’ deficient board diversity claims [updated]
Updated: Red Rock Resorts Inc. disclosed a revised diversity policy on April 26, 2022. Based on those changes, Red Rock Resorts seems to make the goal of diversifying the Board even harder to reach. In the revised policy, Red Rock Resorts stated that, while it is open to recruiting diverse candidates, it would continue to evaluate the benefits of adding new Board members against the additional costs and impact on efficiency that may result from a larger Board—a consideration that it had not stated in its prior policy. See those revisions here and the 2022 policy here. We originally published the content below on January 31, 2022.
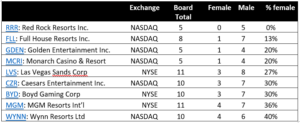
Red Rock is the only one of the nine publicly traded Nevada-based casino gaming companies with zero women on its board of directors. Its five-person board has been the same white men since its 2015 IPO and its justification to shareholders for its board composition relies on deficient claims.
See our letter to the SEC about Red Rock’s deficient board diversity claims here here.
In the Corporate Governance – Diversity section in its 2020 and 2021 proxy filings, Red Rock tells investors that it considers gender among its diversity characteristics and then explains that:
“Gaming regulatory agencies in certain of the jurisdictions in which we operate may require our directors to maintain licenses. The licensing process is onerous, invasive, time consuming and expensive. Because of this, it is difficult to identify well-qualified candidates willing to subject themselves, as well as their families, to the rigorous and intrusive process necessary to obtain a gaming license. As a result of the limited pool of potential directors and the strong qualifications of our present Board, we believe that the current composition of our Board is in the best interest of the Company. We remain continuously open to recruiting well-qualified diverse candidates to our Board.”
There isn’t a limited pool of potential directors for Nevada-based gaming companies
There are several indicators that suggest there is not a limited pool of potential directors for Nevada-based gaming companies. Every publicly traded Nevada-based casino gaming company except Red Rock has at least one woman serving as a director, amounting to 20 out of 76 directors, or 26%, with half of them joining these boards since 2018 [1].
Nationally, women now make up 30% of all directors in the S&P 500, which is up from 28% last year and 16% a decade ago. And in the Russell 3000 index, women of all races account for 27 percent of all directors, up from 24 percent.
The pool of female directors for Nevada casino gaming companies appears to be no smaller than national averages so it is concerning Red Rock justifies its board composition through the problematic idea that if only there were a larger pool of candidates then the Board might look different.
[CHART JANUARY 27, 2022]
A gaming license is not a justifiable obstacle to board diversity
Red Rock’s claims about board diversity also rely on the problematic assumption that the pool of potential directors is too small because of the gaming license process. The gaming license process is not a justifiable obstacle to board diversity, as evidenced by the presence of women on the boards of every publicly traded Nevada-based gaming company except Red Rock.
In fact, at least in Nevada, the licensing process should present no obstacle. Nevada gaming regulation 16.415 does not require licensing of every director of a publicly traded corporation, only of directors who are actively and directly engaged in the administration or supervision of gaming activities. The regulation identifies the board chair and chair of the audit committee as among the directors who must normally be licensed.
Meaning Red Rock can elevate directors to the Board without their undergoing the rigors of the licensing process where they do not require licensing.
Red Rock has an obligation to assess the effectiveness of its diversity policy
Red Rock shareholders deserve to know whether the Company’s diversity policy is effective or not. SEC rule 229.407(c)(2)(vi) states that “if the nominating committee (or the board) has a policy with regard to the consideration of diversity in identifying director nominees, describe how this policy is implemented, as well as how the nominating committee (or the board) assesses the effectiveness of its policy.”
So, what does Red Rock mean when it states in its diversity policy that “we remain continuously open to recruiting well-qualified diverse candidates to our Board”?
Red Rock’s three independent directors, Mr. Robert Cashell Jr., Mr. Robert Lewis, and Mr. James Nave, have been on the Red Rock board since its IPO, comprise the Nominating and Corporate Governance Committee, and were board members of Red Rock’s predecessor company since 2011.
What can the Company disclose to back up the claim that the recruitment of diverse candidates is active and ongoing?
–
NOTE 1:
| COMPANY | DIRECTOR | YEAR JOINED |
| Full House Resorts Inc. | 1 Kathleen M. Marshall | 2007 |
| Golden Entertainment Inc. | 2 Ann N. Dozier | 2019 |
| Monarch Casino & Resort Inc. | 3 Yvette Landau | 2010 |
| Las Vegas Sands Corp. | 4 Micheline Chau | 2014 |
| 5 Nora M. Jordan | 2021 | |
| 6 Yibling Mao | 2021 | |
| Caesars Entertainment Inc. | 7 Bonnie Biumi | 2020 |
| 8 Jan Jones Blackhurst | 2019 | |
| 9 Sandra Douglass Morgan | 2021 | |
| Boyd Gaming Corp. | 10 Marianne Boyd Johnson | 1990 |
| 11 Christine J. Spadafor | 2009 | |
| 12 Veronica Wilson | 2003 | |
| MGM Resorts International | 13 Mary Chris Jammet | 2014 |
| 14 Alexis M. Herman | 2002 | |
| 15 Rose McKinney-James | 2005 | |
| 16 Jan Swartz | 2018 | |
| Wynn Resorts Ltd. | 17 Betsy S. Atkins | 2018 |
| 18 Patricia Mulroy | 2015 | |
| 19 Margaret J. “Dee Dee” Myers | 2018 | |
| 20 Winifred “Wendy” Webb | 2018 |